Introduction
In modern software development, Quality Assurance (QA) has evolved into a strategic practice embedded across the entire software lifecycle from initial requirements to production monitoring. Gone are the days when QA was a late-stage activity; today, quality must be designed in from day one.
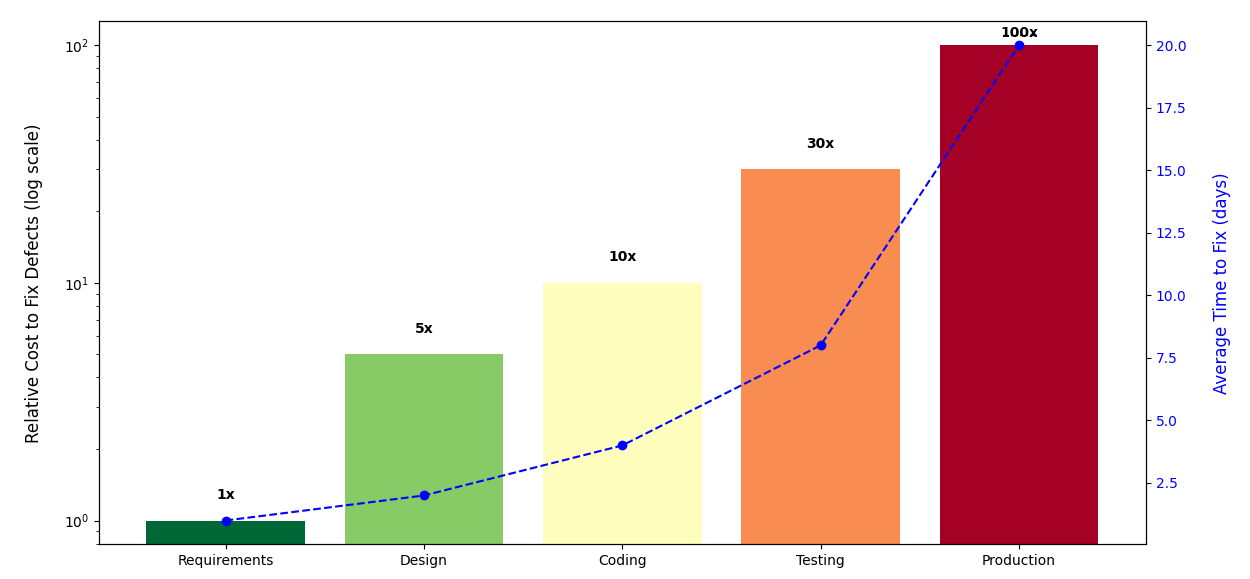
Defects found late are exponentially more costly and disruptive. Still, many teams underestimate the value of integrating QA early, missing out on benefits like better testability, risk mitigation, and smarter design decisions. In fast-paced DevOps and cloud-native environments, QA must move beyond testing and become a key driver of engineering excellence.
This article explores why early QA involvement matters, busts common myths, and offers practical strategies from test derivation to automation, chaos engineering, and the future of AI-driven testing.
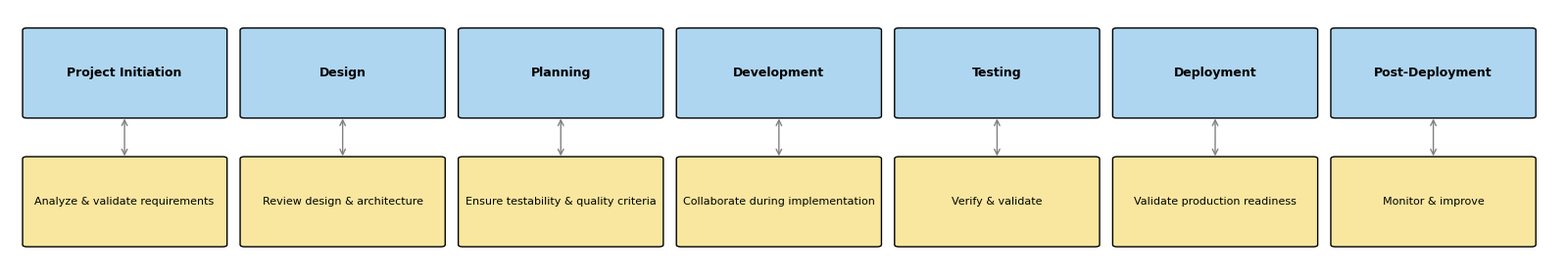
Why QA from Day One?
QA isn’t just about testing it’s about building quality in from the start. Involving QA engineers early ensures:
Clearer requirements
QA clarifies ambiguities and ensures specifications are testable.Better architecture and design
QA promotes maintainable, testable systems with patterns like feature flags, canary releases, and observability.Risk identification
QA spots potential issues in performance, data flows, and security before they become blockers.Reduced costs
Catching defects early reduces rework, testing cycles, and delivery delays delivering strong ROI (Return on Investment).
Common Misconceptions About QA
QA Is Just About Testing
False: QA involves analysis, planning, risk assessment, and continuous improvement.
QA at the End Is Enough
False: Fixing issues late is slower and more expensive. Quality must be built-in early.
QA Doesn’t Need Technical Skills
False: Today’s QA engineers need to understand code, APIs, CI/CD, and system architecture.
QA Is a Cost Center
False: QA prevents expensive bugs, accelerates delivery, and improves customer satisfaction.
Empowering QA Through Technical Proficiency
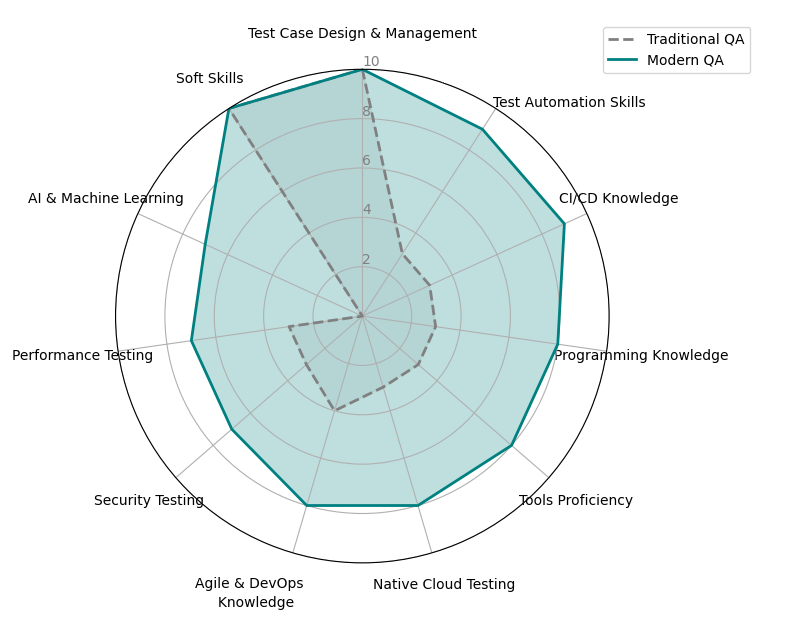
The Role Has Evolved
Modern QA engineers are technical contributors, fluent in:
- Programming and scripting
- Databases, APIs, and infrastructure
- CI/CD pipelines and container orchestration
They bridge development and QA, improving communication and producing high-quality, actionable bug reports.
Collaboration Improves Outcomes
When QA joins early:
- Developers and QA share understanding of feature goals and edge cases
- QA helps design for testability and observability
- Bug resolution is faster, and team morale improves
Organizations that invest in skilled QA engineers enjoy:
- Robust systems
- Faster development cycles
- Higher quality products
Effective Testing Strategies
Beyond Requirements-Based Testing
Requirements often become outdated or miss user expectations. Instead, QA should derive tests from acceptance criteria and real user behavior.
“We were testing what we specified, not what users needed.”
Best Practices for Test Derivation
- Use Given-When-Then format for clarity and automation
- Cover both happy paths and edge cases
- Include non-functional tests (e.g., performance, security)
- Collaborate with developers during test design
“A 30-minute conversation can save days of bug fixing.”
Balancing Test Documentation
- Critical paths: Fully documented
- Core features: Moderate detail
- Edge cases: Exploratory or intent-based notes
Automation and CI/CD Best Practices
Strategic Automation
Not everything should be automated. Focus on:
- High-value regression tests
- Stable APIs and core logic
- Repetitive or error-prone workflows
Avoid over-automating fast-changing UIs or low-impact flows.
Integrated CI/CD Pipelines
Automation is most effective when integrated with CI/CD:
- Unit tests: Fast feedback at commit / pull request stage
- Integration/API tests: Validate system behavior post-merge
- UI, security, and performance tests: Run selectively and periodically
Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing
- Shift-Left: Run tests earlier using TDD, BDD, and static analysis
- Shift-Right: Monitor behavior in production using canary releases and observability tools
Smarter Regression Testing
- Prioritize by risk and recent changes
- Run tests in parallel
- Remove obsolete or flaky tests
Expanding QA with Chaos Engineering
Chaos Engineering introduces intentional failures to validate a system’s resilience especially useful in microservice and cloud-native architectures.
Why It Matters
- Reveals hidden dependencies and cascading failures
- Tests real-world readiness of failovers, self-healing, and monitoring
- Supports recovery planning and operational readiness
Chaos in Practice
- Inject latency, kill services, or simulate network outages
- Monitor the impact and improve recovery mechanisms
Scale tips:
- Enterprise: Automate chaos tests with tools like Gremlin or Chaos Monkey
- Mid-size teams: Focus on critical services
- Smaller teams: Run manual chaos “game days”
Prerequisite: Strong observability is essential to safely run chaos experiments.
The Future of QA: AI and Self-Healing Systems
AI is revolutionizing QA by improving test generation, reducing maintenance, and predicting risk.
AI-Powered Testing
- Generate tests from code, requirements, or user behavior
- Use visual testing, autonomous exploration, and differential comparison
Self-Healing Automation
- Automatically adapts to UI or API changes
- Fixes or flags broken tests using machine learning
- Reduces maintenance by up to 70%
- Tools like browser-use exemplify adaptive, intent-based testing approaches.
Predictive Quality Analytics
- Analyze test data, code changes, and defect history
- Predict high-risk changes and prioritize testing
The Human-AI Combo
While AI offers speed and coverage, human testers provide creativity, intuition, and ethical judgment.
The winning QA formula: Human strategy + AI efficiency
Conclusion
Quality assurance is no longer an isolated phase it’s a strategic enabler of software success. When QA is involved from day one, it drives better requirements, stronger architectures, faster feedback, and resilient systems.
Modern QA is technical, collaborative, and forward-thinking, embracing tools like automation, chaos testing, and AI to meet the demands of today’s software landscape.
Organizations that prioritize QA early, invest in skilled engineers, and align quality with business goals won’t just ship faster they’ll ship better.
"Quality is not an act, it is a habit." – Aristotle
